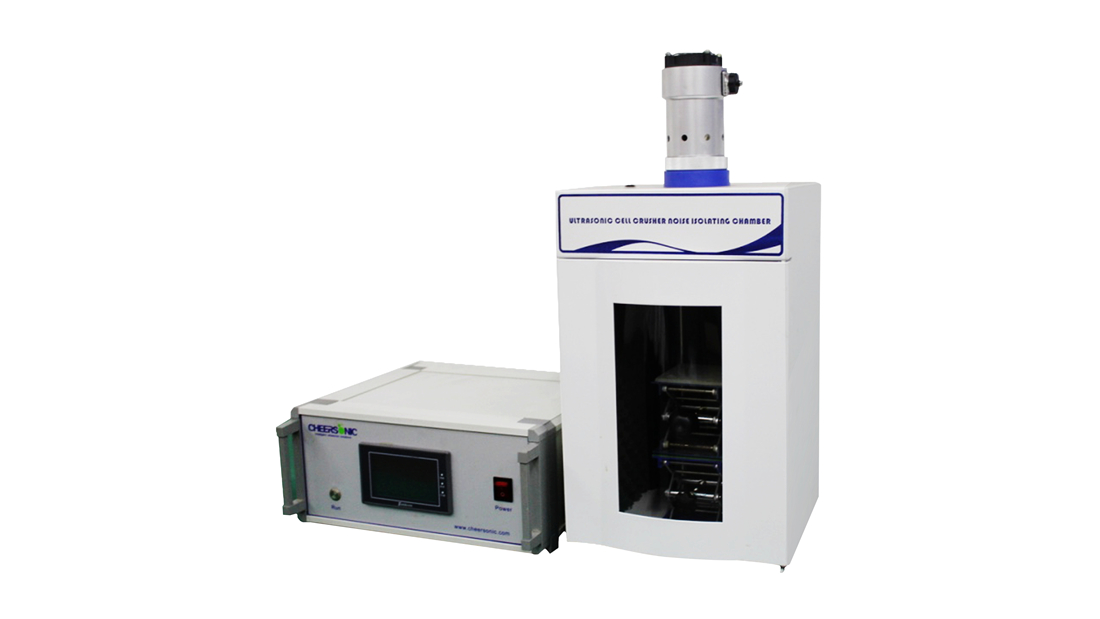
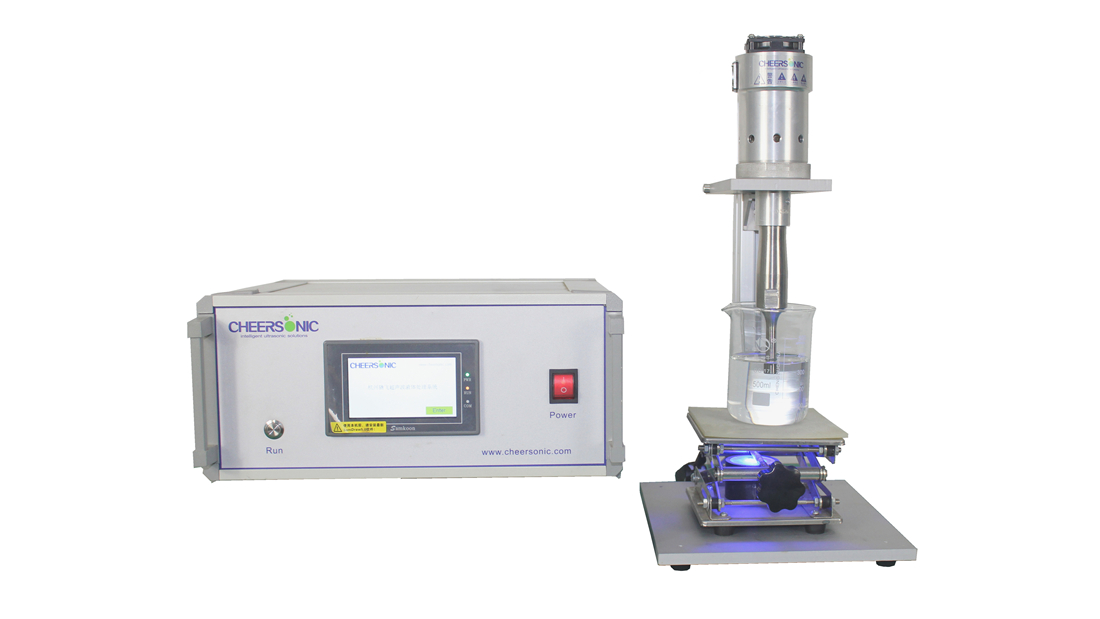
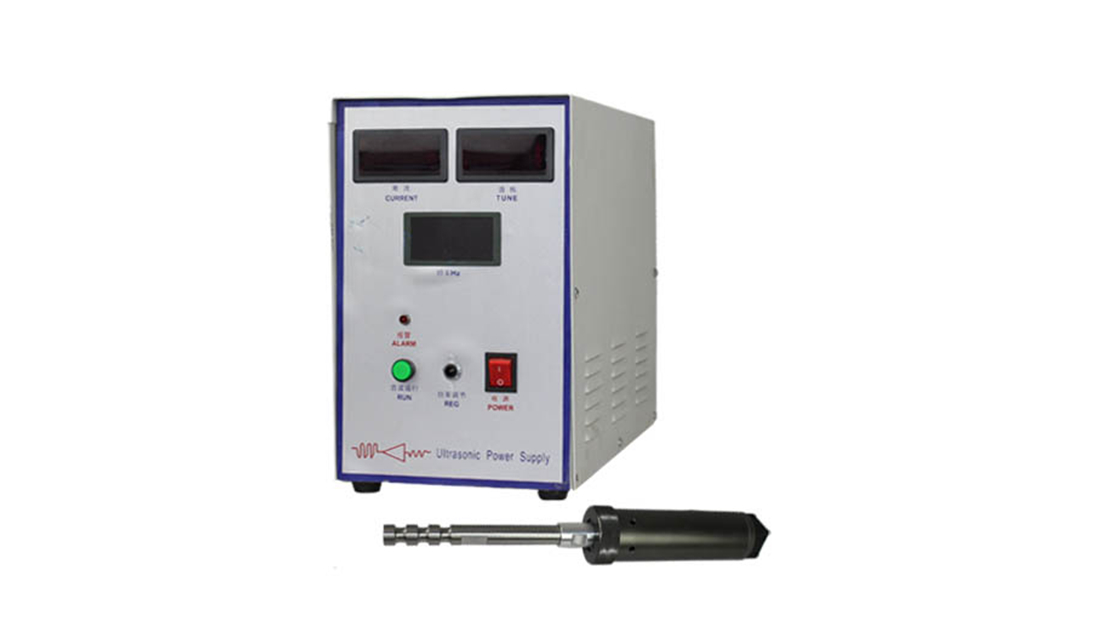
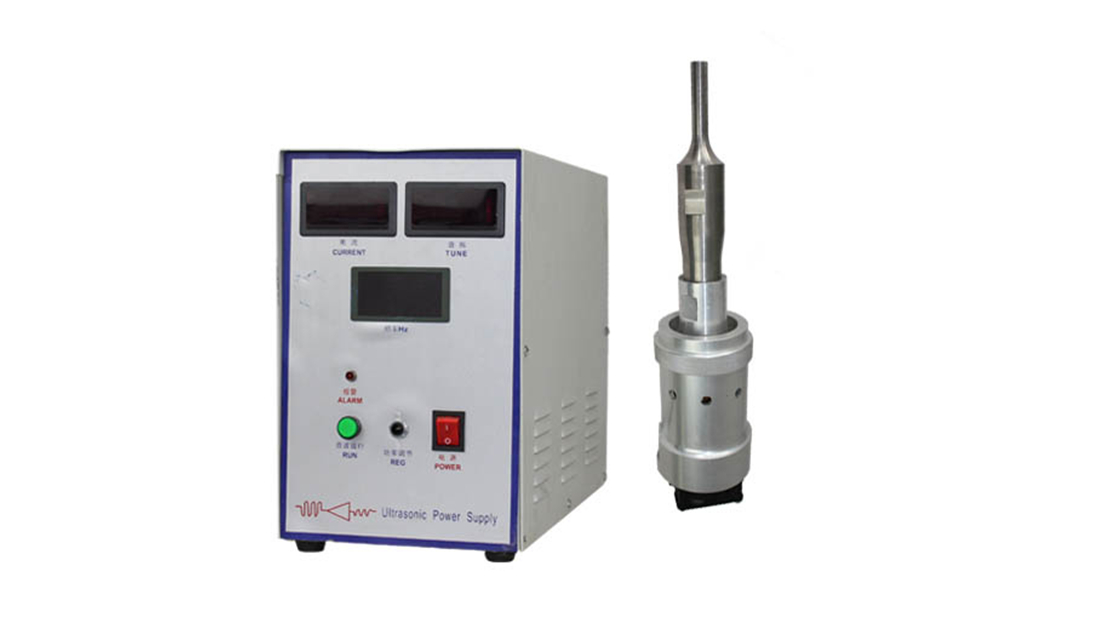
Project Description
Ultrasonics for Vaccine Production
Principle of Ultrasonic Sterilization
Ultrasonics for Vaccine Production. Ultrasound is a sound wave with a frequency greater than 20KHZ, which is a process of propagation of mechanical vibration in a medium. Its high frequency, short wavelength, good directionality, high power, strong penetrating power and so on. Ultrasonic sterilization has proven to be an effective method that can destroy or inactivate viruses and bacteria. The principle of ultrasonic sterilization includes: cavitation, mechanical action, heat action, etc.

Cavitation
The sterilization effect of ultrasound is mainly due to the cavitation produced by ultrasound, which causes the contents of microbial cells to be strongly oscillated, thereby achieving the destruction of microorganisms. Cavitation refers to shock waves generated when sound waves come into contact with liquid media during ultrasonic treatment. These shock waves generate very high temperatures and pressures, which can reach 5500°C and 50000KPa. Using the ultrasonic cavitation effect to produce local instantaneous high temperature and temperature alternating changes, local instantaneous high pressure and pressure changes in the liquid, make certain bacteria in the liquid lethal, inactivate the virus, and even destroy the cell walls of some smaller microorganisms.
Mechanical Action
When the ultrasonic wave propagates in the medium, although the medium particle vibration amplitude is small, but the frequency is high, it can cause huge pressure changes in the medium. This mechanical effect of ultrasonic wave is called mechanical action. Ultrasonic waves propagate in the medium. The particles of the medium are compressed and stretched alternately to form alternating sound pressure, thereby obtaining huge acceleration. The molecules in the medium therefore produce violent movement, causing the movement and change of the volume of tissue cells and the insoluble matter, and the circulation of cell plasmoids. This effect can cause changes in cell function and cause many reactions in the organism. Due to the different mass points of different media, the vibration speed caused by pressure changes is also different.
Heat Effect
Ultrasonic waves act on the medium, causing the molecules of the medium to vibrate violently. Through the interaction between the molecules, the temperature of the medium rises. When ultrasonic waves propagate in body tissues, the heat generated by ultrasonic energy in the body or other media is mainly the result of tissue absorbing sound energy. The thermal effect of ultrasound is different from the diffuse thermal effect of high frequency and other physical factors.
Advantages
Effectively break cell structure, destroy host organisms and cell activity
Precise control of operating parameters that affect cavitation effects
Strong controllability and repeatability
Influencing factors of ultrasonic sterilization
When ultrasound is used alone, there are differences in the sterilization effect under different conditions. The effect of ultrasonic sterilization is mainly affected by factors such as ultrasonic parameters, microbial characteristics and media.
Sound intensity, frequency
When ultrasonic waves act on liquid materials, cavitation effects will be produced. When the sound intensity reaches a certain value, the cavitation bubbles will instantly shrink and collapse sharply. High pressures of hundreds of megapascals and high temperatures of thousands of degrees will be generated in the bubbles.
Low intensity and high power have a better effect on the dispersion of bacterial groups, while high intensity and low power have a stronger killing effect on cells. The higher the frequency, the easier it is to obtain a larger sound intensity. In addition, as the ultrasonic waves propagate in the liquid, the tiny nucleus bubbles in the liquid are activated, and the ultrasonic cavitation effect exhibited by a series of dynamic processes such as shock, contraction, and collapse is also stronger. The more obvious. The general ultrasonic frequency is 20-50kHZ.
Amplitude, sterilization time
In the process of ultrasonic sterilization, the sterilization effect will be affected by the amplitude alignment. Generally speaking, the sterilization effect will be enhanced by increasing the amplitude. As the sterilization time increases. The sterilization effect is roughly proportional to the increase, but if the sterilization time is further increased, the sterilization effect does not increase significantly, but tends to a saturated value. The general sterilization time is set within 10 minutes. As the sterilization time increases, the temperature of the medium will increase, which is unfavorable for the sterilization of some heat-sensitive vaccines.
Types of microorganisms
All pathogenic bacteria have certain resistance to ultrasound, especially when ultrasound is used as a single-eclipse sterilization method. The effect of ultrasound on microorganisms is related to the structure and functional state of the microorganism itself. The killing effect of ultrasound on microorganisms is that it kills bacilli faster than cocci; it kills macrobacteria faster than microbacteria.
Other factors
During sterilization, the temperature of the sample will also affect the sterilization effect. As the temperature rises, the damage effect of ultrasound on bacteria is strengthened. The effect of ultrasound on vaccines of different components in different media will be different.