Heart Stent
Does the heart stent have a life span?
Coronary heart disease is the appearance of plaque in the coronary arteries, which narrows the lumen of the blood vessels, resulting in myocardial ischemia and chest pain.
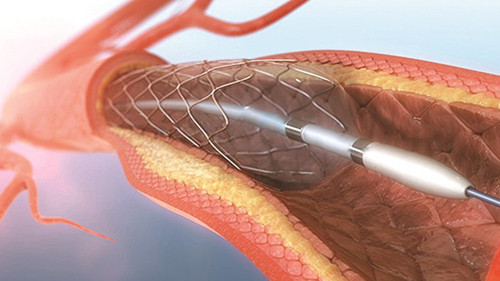
When performing cardiac stent surgery, first use a balloon catheter to expand, flatten the plaque in the blood vessel, and expand the blood vessel at the same time. Then the heart stent is placed. The stent will stick the plaque to the wall of the blood vessel and maintain the size of the blood vessel cavity to prevent the blood vessel from narrowing again due to elastic retraction. The stent and the vascular intima are tightly combined. Subsequently, the endothelial cells on the intima of the blood vessel will slowly grow and gradually cover the stent trabeculae. Eventually, the stent is integrated with the vessel wall. Therefore, there is no such thing as a “lifespan” for heart stents, and heart stents do not need to be replaced every few years. This is a big misunderstanding.

